Where does somatic hypermutation occur
Home » » Where does somatic hypermutation occurYour Where does somatic hypermutation occur images are available. Where does somatic hypermutation occur are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Where does somatic hypermutation occur files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for where does somatic hypermutation occur images information related to the where does somatic hypermutation occur keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
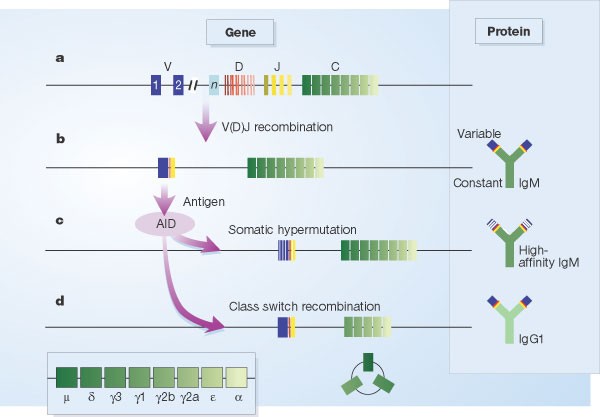
Where Does Somatic Hypermutation Occur. Hypermutation targets a domain around the rearranged V-region which in the K locus extends from the leaderV intron down towards EKiMAR in the J-C intron. Where does somatic recombination occur. It is compelling that some proteins in the canonical base excision and mismatch repair pathways have been hijacked to increase mutagenesis during somatic hypermutation. Somatic hypermutation is a process in which point mutations accumulate in the antibody V-regions of both the heavy and light chains at rates that are about 10 6-fold higher than the background mutation rates observed in other genes Figure 1.
 Aid For Aid Nature From nature.com
Aid For Aid Nature From nature.com
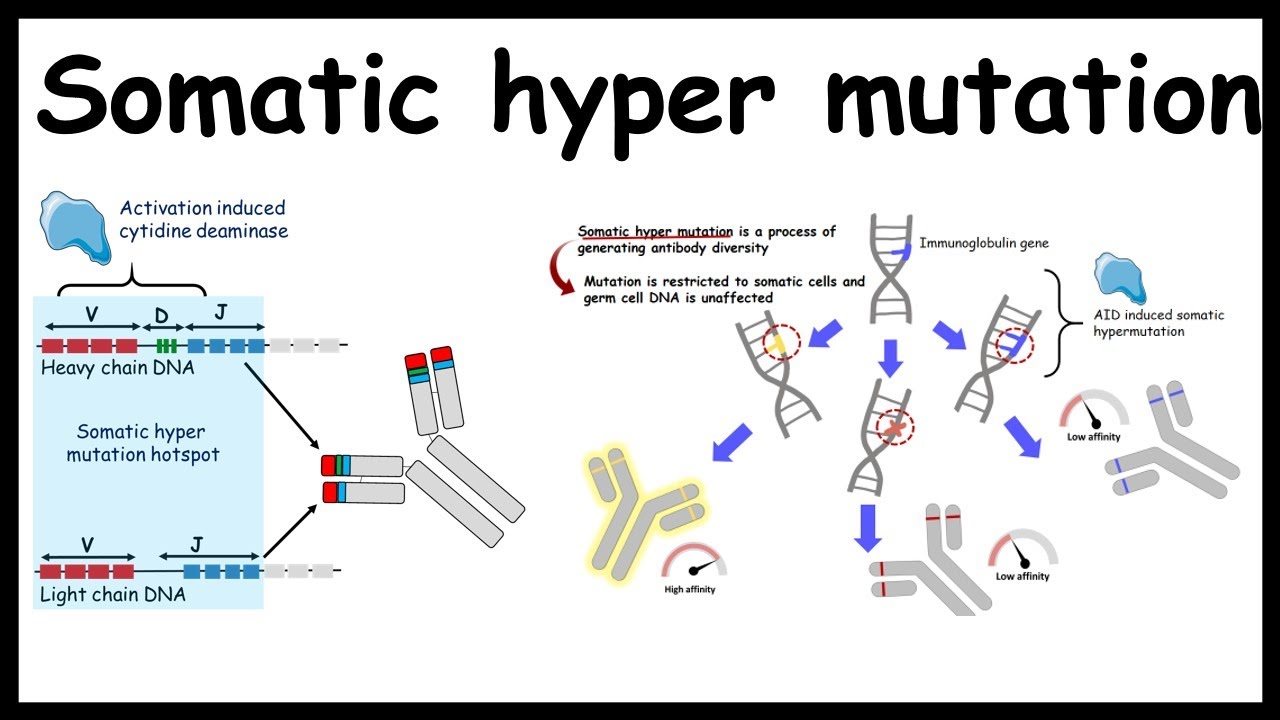
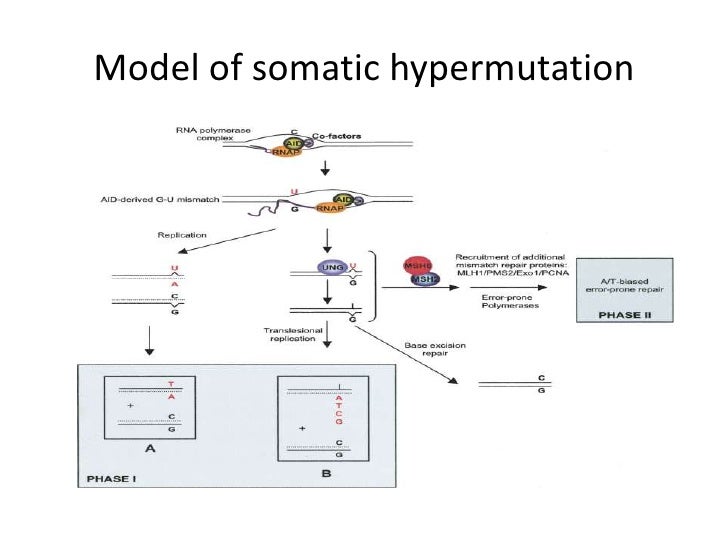
What type of mutations occur for somatic hypermutation to occur nucleotide substitutions at the three CDRs with a frequency of about 1 nucleotide substitution every one or 2 cell divisions what is the purpose of somatic hypermutation. Click to see full answer. Why where by what mechanisms and how does it occur. Activation-induced deaminase AID initiates a flood of DNA damage in the immunoglobulin loci leading to abasic sites single-strand breaks and mismatches. The selection process determining which cells meet this fate appears to occur in stages. Somatic hypermutation SHM is a mechanism by which the immune system adapts in order to recognize antigens that it has not previously encountered.
What type of mutations occur for somatic hypermutation to occur nucleotide substitutions at the three CDRs with a frequency of about 1 nucleotide substitution every one or 2 cell divisions what is the purpose of somatic hypermutation.
1 Occurs only in B cells which are somatic cells does not affect germline DNA 2 The mutations happen very quickly 3 Occurs only after B cells have been activated by cognate Ag and have received T. What type of mutations occur for somatic hypermutation to occur nucleotide substitutions at the three CDRs with a frequency of about 1 nucleotide substitution every one or 2 cell divisions what is the purpose of somatic hypermutation. It is compelling that some proteins in the canonical base excision and mismatch repair pathways have been hijacked to increase mutagenesis during somatic hypermutation. Conclusion Experimental studies have allowed us to gain great insight into the process of somatic hypermutation. Andrea Cross Date. Microbes as seen during class switching.
 Source: febs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: febs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Similarly it is asked how does somatic hypermutation occur. What does somatic hypermutations introd At what location in the germinal centre In the variable regions of both the heavy and light chain Mutations that introduce anywhere from. Somatic hypermutation is the phenomenon in which a high frequency of point mutations are generated within a 12-kb segment in the variable region of expressed immunoglobulin genes in response to the presence of an antigen. Somatic hypermutation or SHM is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it eg. Where does somatic recombination occur.
 Source: immunopaedia.org.za
Source: immunopaedia.org.za
Somatic hypermutation SHM is a mechanism by which the immune system adapts in order to recognize antigens that it has not previously encountered. Activation-induced deaminase AID initiates a flood of DNA damage in the immunoglobulin loci leading to abasic sites single-strand breaks and mismatches. Somatic hypermutation or SHM is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it eg. This mechanism is the predominant method in humans and enables the cells of the immune system to diversify their receptors by promoting mutation. Somatic hypermutation is the phenomenon in which a high frequency of point mutations are generated within a 12-kb segment in the variable region of expressed immunoglobulin genes in response to the presence of an antigen.

Activation-induced deaminase AID initiates a flood of DNA damage in the immunoglobulin loci leading to abasic sites single-strand breaks and mismatches. Activation-induced deaminase AID initiates a flood of DNA damage in the immunoglobulin loci leading to abasic sites single-strand breaks and mismatches. Somatic hypermutation involves a programmed process of mutation affecting the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes. Somatic hypermutation or SHM is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it eg. 1 Occurs only in B cells which are somatic cells does not affect germline DNA 2 The mutations happen very quickly 3 Occurs only after B cells have been activated by cognate Ag and have received T.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
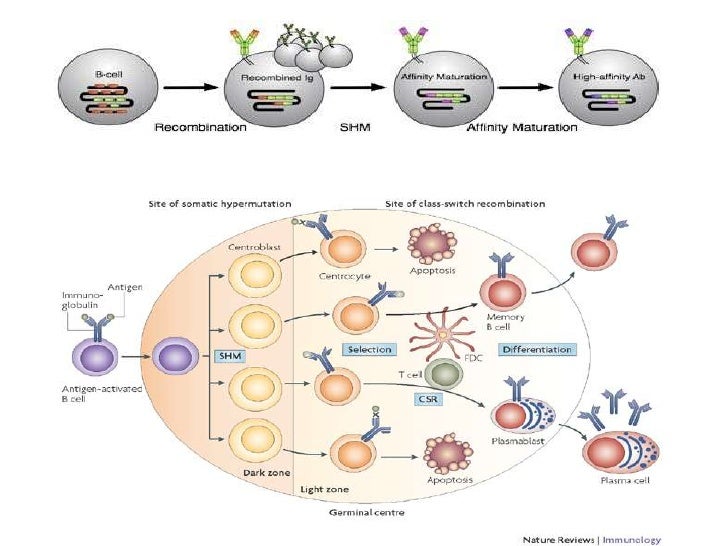
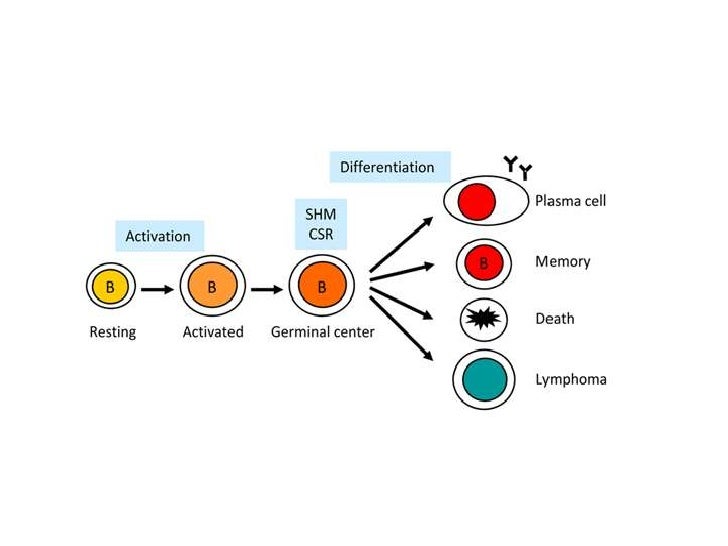
Somatic hypermutation what is affinity maturation Process that selects for B cells producing antibodies of highest affinity to an antigen of interest through successive exposure to. Somatic hypermutation SHM is a mechanism by which the immune system adapts in order to recognize antigens that it has not previously encountered. The selection process determining which cells meet this fate appears to occur in stages. 1 Occurs only in B cells which are somatic cells does not affect germline DNA 2 The mutations happen very quickly 3 Occurs only after B cells have been activated by cognate Ag and have received T. Somatic hypermutation what is affinity maturation Process that selects for B cells producing antibodies of highest affinity to an antigen of interest through successive exposure to.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
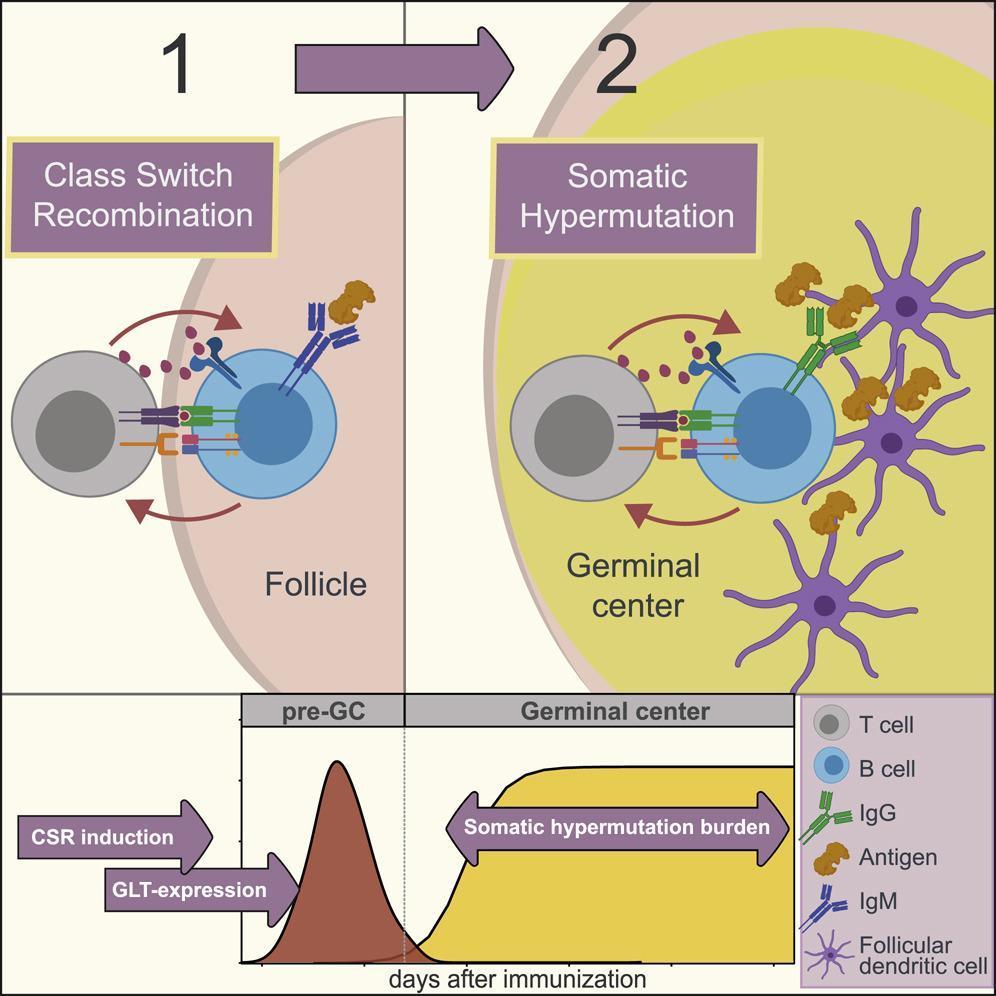
This mechanism is the predominant method in humans and enables the cells of the immune system to diversify their receptors by promoting mutation. Following antigen challenge activated B cells migrate into B cell follicles of secondary lymphatic organs where they undergo rapid expansion and establish oligoclonal germinal centers GCs. Click to see full answer. The mutations are largely nucleotide substitutions with marked substitution preferences in particular a bias towards transitions. It is believed somatic hypermutation occurs in the dark zone of the germinal centre but when centroblasts stop proliferating and develop instead into centrocytes they increase their expression of certain surface receptors and move towards the light zone.
 Source: immunology.org
Source: immunology.org
Somatic hypermutation occurs in the periphery in germinal center follicles of secondary lymphoid organs 9394. Somatic mutation genetic alteration acquired by a cell that can be passed to the progeny of the mutated cell in the course of cell divisionSomatic mutations differ from germ line mutations which are inherited genetic alterations that occur in the germ cells ie sperm and eggsSomatic mutations are frequently caused by environmental factors such as exposure to ultraviolet radiation or. The differentiation of naive B cells into memory B cells occurs within the germinal centers GCs in secondary lymphoid organs where activated naive B cells undergo vigorous proliferation somatic hypermutation of Ig V-region genes isotype switching interaction with antigens antigen-driven selection and differentiation into memory B cells and plasma cells. It is believed somatic hypermutation occurs in the dark zone of the germinal centre but when centroblasts stop proliferating and develop instead into centrocytes they increase their expression of certain surface receptors and move towards the light zone. Somatic hypermutation is the phenomenon in which a high frequency of point mutations are generated within a 12-kb segment in the variable region of expressed immunoglobulin genes in response to the presence of an antigen.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Somatic recombination is different than somatic hypermutation SHM a process that takes place as part of an immune response after a B cell has encountered antigen. Somatic hypermutation what is affinity maturation Process that selects for B cells producing antibodies of highest affinity to an antigen of interest through successive exposure to. Where does somatic recombination occur. Similarly it is asked how does somatic hypermutation occur. Click to see full answer.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Andrea Cross Date. February 10 2021 Somatic cells in the body usually contain the same DNA. Click to see full answer. Following antigen challenge activated B cells migrate into B cell follicles of secondary lymphatic organs where they undergo rapid expansion and establish oligoclonal germinal centers GCs. Somatic hypermutation involves a programmed process of mutation affecting the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Andrea Cross Date. This mechanism is the predominant method in humans and enables the cells of the immune system to diversify their receptors by promoting mutation. Similarly it is asked how does somatic hypermutation occur. Somatic hypermutation occurs in the periphery in germinal center follicles of secondary lymphoid organs 9394. What type of mutations occur for somatic hypermutation to occur nucleotide substitutions at the three CDRs with a frequency of about 1 nucleotide substitution every one or 2 cell divisions what is the purpose of somatic hypermutation.
 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
Following antigen challenge activated B cells migrate into B cell follicles of secondary lymphatic organs where they undergo rapid expansion and establish oligoclonal germinal centers GCs. Somatic hypermutation or SHM is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it eg. Somatic hypermutation occurs in the periphery in germinal center follicles of secondary lymphoid organs 9394. Somatic mutation genetic alteration acquired by a cell that can be passed to the progeny of the mutated cell in the course of cell divisionSomatic mutations differ from germ line mutations which are inherited genetic alterations that occur in the germ cells ie sperm and eggsSomatic mutations are frequently caused by environmental factors such as exposure to ultraviolet radiation or. Following antigen challenge activated B cells migrate into B cell follicles of secondary lymphatic organs where they undergo rapid expansion and establish oligoclonal germinal centers GCs.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Somatic recombination occurs prior to antigen contact during B. Click to see full answer. Somatic hypermutation what is affinity maturation Process that selects for B cells producing antibodies of highest affinity to an antigen of interest through successive exposure to. Microbes as seen during class switching. Somatic hypermutation is a process in which point mutations accumulate in the antibody V-regions of both the heavy and light chains at rates that are about 10 6-fold higher than the background mutation rates observed in other genes Figure 1.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Microbes as seen during class switching. Conclusion Experimental studies have allowed us to gain great insight into the process of somatic hypermutation. Antibodies created by this process can have markedly increased affinities for self-antigens. Somatic hypermutation or SHM is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it eg. Click to see full answer.
 Source: osmosis.org
Source: osmosis.org
Conclusion Experimental studies have allowed us to gain great insight into the process of somatic hypermutation. Somatic hypermutation or SHM is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it eg. Why where by what mechanisms and how does it occur. Microbes as seen during class switching. What does somatic hypermutations introd At what location in the germinal centre In the variable regions of both the heavy and light chain Mutations that introduce anywhere from.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Somatic hypermutation is a process in which point mutations accumulate in the antibody V-regions of both the heavy and light chains at rates that are about 10 6-fold higher than the background mutation rates observed in other genes Figure 1. Antibodies created by this process can have markedly increased affinities for self-antigens. Microbes as seen during class switching. Following antigen challenge activated B cells migrate into B cell follicles of secondary lymphatic organs where they undergo rapid expansion and establish oligoclonal germinal centers GCs. What type of mutations occur for somatic hypermutation to occur nucleotide substitutions at the three CDRs with a frequency of about 1 nucleotide substitution every one or 2 cell divisions what is the purpose of somatic hypermutation.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Somatic recombination occurs prior to antigen contact during B. Somatic recombination is different than somatic hypermutation SHM a process that takes place as part of an immune response after a B cell has encountered antigen. The differentiation of naive B cells into memory B cells occurs within the germinal centers GCs in secondary lymphoid organs where activated naive B cells undergo vigorous proliferation somatic hypermutation of Ig V-region genes isotype switching interaction with antigens antigen-driven selection and differentiation into memory B cells and plasma cells. Activation-induced deaminase AID initiates a flood of DNA damage in the immunoglobulin loci leading to abasic sites single-strand breaks and mismatches. Somatic hypermutation or SHM is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it eg.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
1 Occurs only in B cells which are somatic cells does not affect germline DNA 2 The mutations happen very quickly 3 Occurs only after B cells have been activated by cognate Ag and have received T. February 10 2021 Somatic cells in the body usually contain the same DNA. 1 Occurs only in B cells which are somatic cells does not affect germline DNA 2 The mutations happen very quickly 3 Occurs only after B cells have been activated by cognate Ag and have received T. It is believed somatic hypermutation occurs in the dark zone of the germinal centre but when centroblasts stop proliferating and develop instead into centrocytes they increase their expression of certain surface receptors and move towards the light zone. Somatic hypermutation is the phenomenon in which a high frequency of point mutations are generated within a 12-kb segment in the variable region of expressed immunoglobulin genes in response to the presence of an antigen.
 Source: osmosis.org
Source: osmosis.org
Microbes as seen during class switching. Somatic hypermutation is a process in which point mutations accumulate in the antibody V-regions of both the heavy and light chains at rates that are about 10 6-fold higher than the background mutation rates observed in other genes Figure 1. Hypermutation targets a domain around the rearranged V-region which in the K locus extends from the leaderV intron down towards EKiMAR in the J-C intron. It is compelling that some proteins in the canonical base excision and mismatch repair pathways have been hijacked to increase mutagenesis during somatic hypermutation. Similarly it is asked how does somatic hypermutation occur.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
What type of mutations occur for somatic hypermutation to occur nucleotide substitutions at the three CDRs with a frequency of about 1 nucleotide substitution every one or 2 cell divisions what is the purpose of somatic hypermutation. Somatic hypermutation is a process in which point mutations accumulate in the antibody V-regions of both the heavy and light chains at rates that are about 10 6-fold higher than the background mutation rates observed in other genes Figure 1. This accumulation of mutations at the V-region genes occurs at the centroblast stage of B-cell differentiation in the germinal centers of secondary lymphoid organs. Andrea Cross Date. Click to see full answer.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title where does somatic hypermutation occur by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.