Late sodium current
Home » » Late sodium currentYour Late sodium current images are ready in this website. Late sodium current are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Late sodium current files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for late sodium current pictures information connected with to the late sodium current keyword, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Late Sodium Current. Late sodium current inhibition alone with ranolazine is sufficient to reduce ischemia- and cardiac glycoside-induced calcium overload and contractile dysfunction mediated by reverse-mode sodiumcalcium exchange. It remains possible to consider both early Na currents and potentially arrhythmogenic I. Role of late sodium current in modulating the proarrhythmic and antiarrhythmic effects of quinidine. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block.
 Phases Of Cardiac Action Potential Nursing School Tips Medical Studies Critical Care Nursing From pinterest.com
Phases Of Cardiac Action Potential Nursing School Tips Medical Studies Critical Care Nursing From pinterest.com
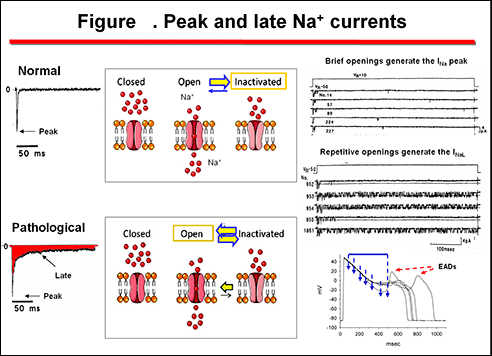
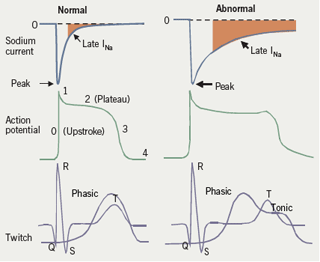
1Although under normal conditions it is a small current 05 relative to peak I Na it is sufficiently large during the AP plateau to affect the duration and the flow over hundreds of milliseconds during the AP contributes more to. INalate was also reported to play a role in chronic atrial fibrillation AF. Calcium overload in ischemic cells leads to impaired relaxation which increases ventricular diastolic wall stress and end-diastolic pressure. Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. In the ischemic myocardium late inward sodium currents contribute to an elevation in intracellular sodium which leads to an increase in intracellular calcium through the sodium-calcium exchanger. The sodium current peaks at the onset of the action potential and continues throughout systole with a so-called late component or late I Na see figure 1 which decays gradually.
Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways.
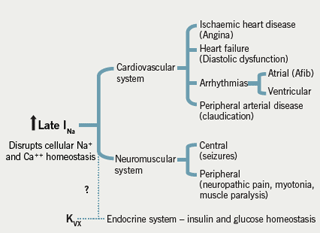
INalate was also reported to play a role in chronic atrial fibrillation AF. Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases. As recently appreciated common neurological and cardiac conditions are associated with abnormal I NaL enhancement which may contribute to the pathogenesis of both electrical and contractile dysfunction. Late sodium current is pathologically increased in both genetic and acquired heart disease making it an attractive target for therapy to treat arrhythmia heart failure and angina. The first goal of this article is to describe how I Nalate functions under physiological circumstances. 1Although under normal conditions it is a small current 05 relative to peak I Na it is sufficiently large during the AP plateau to affect the duration and the flow over hundreds of milliseconds during the AP contributes more to.
 Source: physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
1Pharmacological Sciences CV Therapeutics Inc. By causing repolarisation failure early afterdepolarisations. INalate was also reported to play a role in chronic atrial fibrillation AF. Late sodium current in cardiac cells is very small compared with the fast component but as it flows throughout the action potential it may make a substantial contribution to sodium loading during each cardiac cycle. 1Although under normal conditions it is a small current 05 relative to peak I Na it is sufficiently large during the AP plateau to affect the duration and the flow over hundreds of milliseconds during the AP contributes more to.
 Source: id.pinterest.com
Source: id.pinterest.com
Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases. Role of late sodium current in modulating the proarrhythmic and antiarrhythmic effects of quinidine. By causing repolarisation failure early afterdepolarisations. This clinical trial demonstrates that late sodium blocking drugs can substantially reduce QTc prolongation from hERG potassium channel block and assessment of J-Tpeak c may add value beyond only assessing QTc. In the ischemic myocardium late inward sodium currents contribute to an elevation in intracellular sodium which leads to an increase in intracellular calcium through the sodium-calcium exchanger.
 Source: drsvenkatesan.com
Source: drsvenkatesan.com
Late Sodium Current in Human Atrial Cardiomyocytes from Patients in Sinus Rhythm and Atrial Fibrillation. The Cardiac Late Sodium Channel Current is a Molecular Target for the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Circulation. The first goal of this article is to describe how I Nalate functions under physiological circumstances. Known as late Na currents I Na-L occur under physiological conditions during the cardiac AP. Late sodium current is pathologically increased in both genetic and acquired heart disease making it an attractive target for therapy to treat arrhythmia heart failure and angina.
 Source: itaca.edu.es
Source: itaca.edu.es
Late sodium current in cardiac cells is very small compared with the fast component but as it flows throughout the action potential it may make a substantial contribution to sodium loading during each cardiac cycle. Late sodium current I NaL is a small sustained inward current observed during the cardiac action potential plateau phase following decay of the early peak I Na. Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases. The first goal of this article is to describe how I Nalate functions under physiological circumstances. Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways.
 Source: tmedweb.tulane.edu
Source: tmedweb.tulane.edu
This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block. Late sodium current inhibition alone with ranolazine is sufficient to reduce ischemia- and cardiac glycoside-induced calcium overload and contractile dysfunction mediated by reverse-mode sodiumcalcium exchange. 1Pharmacological Sciences CV Therapeutics Inc. It is responsible in part for maintaining the plateau of the action potential and it is therefore. Known as late Na currents I Na-L occur under physiological conditions during the cardiac AP.
 Source: cvpharmacology.com
Source: cvpharmacology.com
Online ahead of print. Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. Late sodium current is pathologically increased in both genetic and acquired heart disease making it an attractive target for therapy to treat arrhythmia heart failure and angina. Wu L1 Guo D Li H Hackett J Yan GX Jiao Z Antzelevitch C Shryock JC Belardinelli L. Furthermore all QTc shortening occurs in the heart-rate corrected J-Tpeak J-Tpeak c interval the biomarker we identified as a sign of late sodium current block.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Furthermore all QTc shortening occurs in the heart-rate corrected J-Tpeak J-Tpeak c interval the biomarker we identified as a sign of late sodium current block. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block. This clinical trial demonstrates that late sodium blocking drugs can substantially reduce QTc prolongation from hERG potassium channel block and assessment of J-Tpeak c may add value beyond only assessing QTc. The sodium current peaks at the onset of the action potential and continues throughout systole with a so-called late component or late I Na see figure 1 which decays gradually. The first goal of this article is to describe how I Nalate functions under physiological circumstances.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Furthermore all QTc shortening occurs in the heart-rate corrected J-Tpeak J-Tpeak c interval the biomarker we identified as a sign of late sodium current block. Late sodium current in cardiac cells is very small compared with the fast component but as it flows throughout the action potential it may make a substantial contribution to sodium loading during each cardiac cycle. The Cardiac Late Sodium Channel Current is a Molecular Target for the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Circulation. Late sodium current I NaL is a small sustained inward current observed during the cardiac action potential plateau phase following decay of the early peak I Na. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In the ischemic myocardium late inward sodium currents contribute to an elevation in intracellular sodium which leads to an increase in intracellular calcium through the sodium-calcium exchanger. The Cardiac Late Sodium Channel Current is a Molecular Target for the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Circulation. Role of late sodium current in modulating the proarrhythmic and antiarrhythmic effects of quinidine. The sodium current peaks at the onset of the action potential and continues throughout systole with a so-called late component or late I Na see figure 1 which decays gradually. INalate was also reported to play a role in chronic atrial fibrillation AF.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The sodium current peaks at the onset of the action potential and continues throughout systole with a so-called late component or late I Na see figure 1 which decays gradually. The Cardiac Late Sodium Channel Current is a Molecular Target for the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Circulation. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block. Role of late sodium current in modulating the proarrhythmic and antiarrhythmic effects of quinidine. Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Known as late Na currents I Na-L occur under physiological conditions during the cardiac AP. Late Sodium Current in Human Atrial Cardiomyocytes from Patients in Sinus Rhythm and Atrial Fibrillation. The late sodium current I NaL is a sustained component of the fast Na current of cardiac myocytes and neurons. Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. Late sodium current in cardiac cells is very small compared with the fast component but as it flows throughout the action potential it may make a substantial contribution to sodium loading during each cardiac cycle.
 Source: itaca.edu.es
Source: itaca.edu.es
It is responsible in part for maintaining the plateau of the action potential and it is therefore. The Cardiac Late Sodium Channel Current is a Molecular Target for the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Circulation. Late sodium current I NaL is a small sustained inward current observed during the cardiac action potential plateau phase following decay of the early peak I Na. Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. Late sodium current inhibition alone with ranolazine is sufficient to reduce ischemia- and cardiac glycoside-induced calcium overload and contractile dysfunction mediated by reverse-mode sodiumcalcium exchange.
 Source: bjcardio.co.uk
Source: bjcardio.co.uk
The late sodium current I NaL is a sustained component of the fast Na current of cardiac myocytes and neurons. Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases. The first goal of this article is to describe how I Nalate functions under physiological circumstances. Calcium overload in ischemic cells leads to impaired relaxation which increases ventricular diastolic wall stress and end-diastolic pressure. By causing repolarisation failure early afterdepolarisations.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases. The sodium current peaks at the onset of the action potential and continues throughout systole with a so-called late component or late I Na see figure 1 which decays gradually. The Cardiac Late Sodium Channel Current is a Molecular Target for the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Circulation. It remains possible to consider both early Na currents and potentially arrhythmogenic I. INalate was also reported to play a role in chronic atrial fibrillation AF.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases. It is responsible in part for maintaining the plateau of the action potential and it is therefore. Late Sodium Current in Human Atrial Cardiomyocytes from Patients in Sinus Rhythm and Atrial Fibrillation. Known as late Na currents I Na-L occur under physiological conditions during the cardiac AP.
 Source: cvpharmacology.com
Source: cvpharmacology.com
Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. The second goal is to show the. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block. Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases. Large and growing body of data suggest that an increased late sodium current I Nalate can have a significant pathophysiological role in heart failure and other heart diseases.
 Source: bjcardio.co.uk
Source: bjcardio.co.uk
This clinical trial demonstrates that late sodium blocking drugs can substantially reduce QTc prolongation from hERG potassium channel block and assessment of J-Tpeak c may add value beyond only assessing QTc. Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. Online ahead of print. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block.
 Source: cz.pinterest.com
Source: cz.pinterest.com
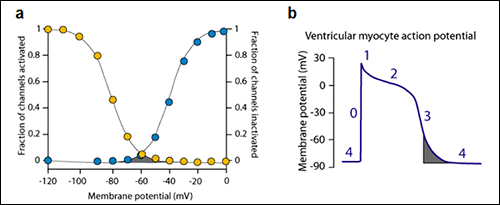
Late sodium current may contribute to triggering arrhythmia in two ways. This review provides an overview of the underlying bases for the clinical implications of late sodium current block. In the ischemic myocardium late inward sodium currents contribute to an elevation in intracellular sodium which leads to an increase in intracellular calcium through the sodium-calcium exchanger. 1Although under normal conditions it is a small current 05 relative to peak I Na it is sufficiently large during the AP plateau to affect the duration and the flow over hundreds of milliseconds during the AP contributes more to. Late sodium current I Na is the residual I Na fl owing after the large peak I Na during an action potential AP or voltage clamp Fig.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title late sodium current by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.