Intracranial vascular calcifications
Home » » Intracranial vascular calcificationsYour Intracranial vascular calcifications images are available in this site. Intracranial vascular calcifications are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Intracranial vascular calcifications files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for intracranial vascular calcifications images information linked to the intracranial vascular calcifications topic, you have come to the right site. Our website always gives you suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Intracranial Vascular Calcifications. Lead poisoning should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unexplained. Other causes of vascular intracranial calcifications include. Pathological intracranial calcification can be divided into infectious congenital endocrinemetabolic vascular and neoplastic. Middle cerebral artery 5.

Some calcifications are common and viewed as innocent whereas others are strong predictors of adverse clinical outcomes including stroke transient ischemic attacks epileptic seizures and cognitive decline 1 2 3 4. Intracranial arterial calcifications are a common incidental finding on computed tomography CT imaging in the general population. Intracranial arterial calcification IAC is an easily identifiable entity on plain head computed tomography scans. Pathological intracranial calcification can be divided into infectious congenital endocrinemetabolic vascular and neoplastic. The two most commonly encountered types of calcification include. The prevalence of intracranial artery calcification are.
Some calcifications are common and viewed as innocent whereas others are strong predictors of adverse clinical outcomes including stroke transient ischemic attacks epileptic seizures and cognitive decline 1 2 3 4.
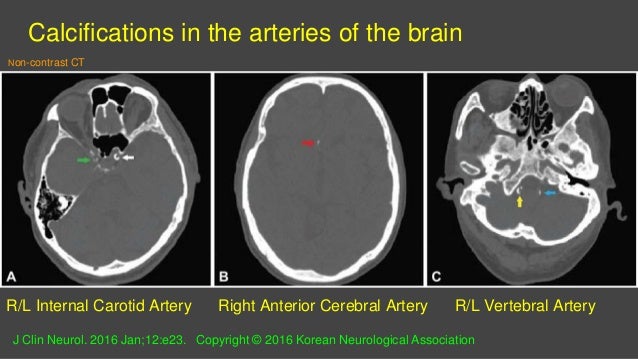
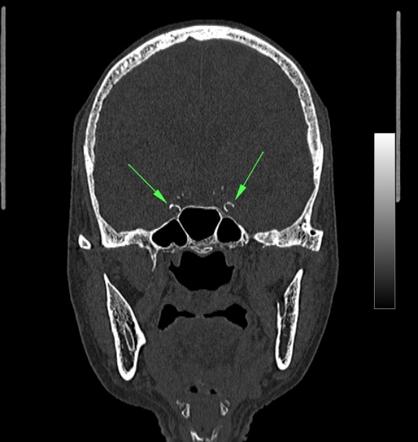
Their prevalence ranges from 1 in young individuals to up to 20 in elderly. Arteriosclerotic calcifications of the internal carotid arteries typically are seen in the parasellar region where the arteries pass through the cavernous sinuses. Intracranial calcifications are common in certain locations and often are of no clinical concern. Lead poisoning should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unexplained. Intimal calcifications are associated with blocked arteries and blood clots. Basal ganglia and cortical calcifications are common features of all infections that constitute the TORCH syndrome toxoplasmosis other rubella cytomegalovirus herpes simplex virus.

Middle cerebral artery 5. The term physiological calcification is used to indicate calcification when seen as part of normal ageing. Each location has different associated risks. Intracranial arterial calcifications are a common incidental finding on computed tomography CT imaging in the general population. The latter findings support the concept of dystrophic calcification following lead-induced cerebrovascular injury.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Arteriosclerotic calcifications of the internal carotid arteries typically are seen in the parasellar region where the arteries pass through the cavernous sinuses. Intimal calcifications are associated with blocked arteries and blood clots. Normal age-related intracranial calcifications. Intracranial calcifications are common in patients with congenital infections but their appearance is not specific because they reflect dystrophic calcifications similar to any chronic brain injury. Some calcifications are common and viewed as innocent whereas others are strong predictors of adverse clinical outcomes including stroke transient ischemic attacks epileptic seizures and cognitive decline 1 2 3 4.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
The prevalence of intracranial artery calcification are. Calcifications can occur in the intimal inside or medial middle layer part of the blood vessel. Intracranial calcifications are common in patients with congenital infections but their appearance is not specific because they reflect dystrophic calcifications similar to any chronic brain injury. CT scans showed a high-grade glioma and extensive intracranial calcifications which proved to be vascular in distribution on postmortem examination. Other causes of vascular intracranial calcifications include.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Basal ganglia and cortical calcifications are common features of all infections that constitute the TORCH syndrome toxoplasmosis other rubella cytomegalovirus herpes simplex virus. Whereas certain calcifications are considered an incidental finding their presence can sometimes be crucial in making a specific diagnosis. However brain calcifications were reported in up to 72 in autopsy cases with microscopic calcifications being the most common 2. The pathogenesis is diverse and ranges from benign physiological calcifications to a variety of pathological disorders. Intracranial arterial calcification IAC is an easily identifiable entity on plain head computed tomography scans.

Whereas certain calcifications are considered an incidental finding their presence can sometimes be crucial in making a specific diagnosis. The latter findings support the concept of dystrophic calcification following lead-induced cerebrovascular injury. Arteriosclerotic calcifications of the internal carotid arteries typically are seen in the parasellar region where the arteries pass through the cavernous sinuses. Recent studies have found high prevalence rates for IAC worldwide and this may be associated with ischemic stroke and cognitive decline. Intracranial calcifications seen on computed tomography CT are the most common finding in the everyday practice of neuroradiology because noncontrast-enhanced CT of the head is the preferred imaging modality worldwide for the initial evaluation of patients with acute or chronic neurological problems.
 Source: atherosclerosis-journal.com
Source: atherosclerosis-journal.com
Recent studies have found high prevalence rates for IAC worldwide and this may be associated with ischemic stroke and cognitive decline. In Part 2 the chief focus is on discussing endocrinemetabolic vascular and neoplastic intracranial calcification etiologies of intracranial calcification. Lead poisoning should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unexplained. Concerning calcifications are much less common and occur in a variety of settings including 3. Each location has different associated risks.

Middle cerebral artery 5. CT scans showed a high-grade glioma and extensive intracranial calcifications which proved to be vascular in distribution on postmortem examination. Intimal calcifications are associated with blocked arteries and blood clots. Intracranial arterial calcification IAC is an easily identifiable entity on plain head computed tomography scans. Brain calcifications are a common radiographic finding.

Vascular calcifications in a young woman can be seen in diabetes mellitus and conditions which accelerate hardening of the arteries throughout the bod. Calcification of the intracranial arteries associated with primary atherosclerosis is more frequent in elderly people. Including aneurysm arteriosclerosis and arteriovenous malformations which are common vascular causes of intracranial calcification. Lead poisoning should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unexplained. Recent studies have found high prevalence rates for IAC worldwide and this may be associated with ischemic stroke and cognitive decline.

Intimal calcifications are associated with blocked arteries and blood clots. Intracranial calcification ICC refers to calcification within the cranial cavity and is generally taken to mean calcification within the parenchyma of the brain or its vasculature. Vascular calcifications in a young woman can be seen in diabetes mellitus and conditions which accelerate hardening of the arteries throughout the bod. By contrast an aneurysm is more often in a suprasellar location and therefore is suspected when a sellar pattern of. Lead poisoning should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unexplained.
 Source: cjasn.asnjournals.org
Source: cjasn.asnjournals.org
Intracranial arterial calcifications are a common incidental finding on computed tomography CT imaging in the general population. Pathological intracranial calcification can be divided into infectious congenital endocrinemetabolic vascular and neoplastic. Brain calcifications are a common radiographic finding. By contrast an aneurysm is more often in a suprasellar location and therefore is suspected when a sellar pattern of. Other causes of vascular intracranial calcifications include.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
In Part 2 the chief focus is on discussing endocrinemetabolic vascular and neoplastic intracranial calcification etiologies of intracranial calcification. Furthermore although intracranial artery calcification. Normal age-related intracranial calcifications. Calcification of the intracranial arteries associated with primary atherosclerosis is more frequent in elderly people. Intracranial arterial calcifications are a common incidental finding on computed tomography CT imaging in the general population.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Intracranial arterial calcification IAC is an easily identifiable entity on plain head computed tomography scans. Calcification of the intracranial arteries associated with primary atherosclerosis is more frequent in elderly people. Other causes of vascular intracranial calcifications include. The term physiological calcification is used to indicate calcification when seen as part of normal ageing. Each location has different associated risks.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
By contrast an aneurysm is more often in a suprasellar location and therefore is suspected when a sellar pattern of. The two most commonly encountered types of calcification include. Intracranial calcifications are common in patients with congenital infections but their appearance is not specific because they reflect dystrophic calcifications similar to any chronic brain injury. Brain calcifications are a common radiographic finding. Intracranial calcifications seen on computed tomography CT are the most common finding in the everyday practice of neuroradiology because noncontrast-enhanced CT of the head is the preferred imaging modality worldwide for the initial evaluation of patients with acute or chronic neurological problems.
 Source: atherosclerosis-journal.com
Source: atherosclerosis-journal.com
The term physiological calcification is used to indicate calcification when seen as part of normal ageing. However brain calcifications were reported in up to 72 in autopsy cases with microscopic calcifications being the most common 2. The term physiological calcification is used to indicate calcification when seen as part of normal ageing. In Part 2 the chief focus is on discussing endocrinemetabolic vascular and neoplastic intracranial calcification etiologies of intracranial calcification. Normal age-related intracranial calcifications.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Intracranial calcifications are common in certain locations and often are of no clinical concern. However brain calcifications were reported in up to 72 in autopsy cases with microscopic calcifications being the most common 2. Middle cerebral artery 5. By contrast an aneurysm is more often in a suprasellar location and therefore is suspected when a sellar pattern of. Intracranial calcifications seen on computed tomography CT are the most common finding in the everyday practice of neuroradiology because noncontrast-enhanced CT of the head is the preferred imaging modality worldwide for the initial evaluation of patients with acute or chronic neurological problems.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Intracranial calcification ICC refers to calcification within the cranial cavity and is generally taken to mean calcification within the parenchyma of the brain or its vasculature. Intimal calcifications are associated with blocked arteries and blood clots. In Part 2 the chief focus is on discussing endocrinemetabolic vascular and neoplastic intracranial calcification etiologies of intracranial calcification. Some calcifications are common and viewed as innocent whereas others are strong predictors of adverse clinical outcomes including stroke transient ischemic attacks epileptic seizures and cognitive decline 1 2 3 4. Vascular calcifications in a young woman can be seen in diabetes mellitus and conditions which accelerate hardening of the arteries throughout the bod.
 Source: strokejournal.org
Source: strokejournal.org
Medial calcifications for example are most often associated with kidney disease diabetes hypertension and advanced age. CT scans showed a high-grade glioma and extensive intracranial calcifications which proved to be vascular in distribution on postmortem examination. Medial calcifications for example are most often associated with kidney disease diabetes hypertension and advanced age. Lead poisoning should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unexplained. Arteriosclerotic calcifications of the internal carotid arteries typically are seen in the parasellar region where the arteries pass through the cavernous sinuses.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Intracranial calcifications are common in patients with congenital infections but their appearance is not specific because they reflect dystrophic calcifications similar to any chronic brain injury. Arteriosclerotic calcifications of the internal carotid arteries typically are seen in the parasellar region where the arteries pass through the cavernous sinuses. The two most commonly encountered types of calcification include. Basal ganglia and cortical calcifications are common features of all infections that constitute the TORCH syndrome toxoplasmosis other rubella cytomegalovirus herpes simplex virus. Medial calcifications for example are most often associated with kidney disease diabetes hypertension and advanced age.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title intracranial vascular calcifications by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.