Hemodynamic response function
Home » » Hemodynamic response functionYour Hemodynamic response function images are ready in this website. Hemodynamic response function are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Hemodynamic response function files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for hemodynamic response function pictures information related to the hemodynamic response function interest, you have visit the right blog. Our site always gives you hints for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Hemodynamic Response Function. Accurately model the hemodynamic response function HRF ie the hemodynamic response evoked by a punctuate neural event. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI is a medical-imaging technique for studying brain function. FMRI is the convolution of the hemodynamic response function HRF and unmeasured neural activity. Lets assume for now that the voxel is also activated to an equal degree to all stimuli.
 Stress Response Regulation And The Hemodynamic Response Pnas From pnas.org
Stress Response Regulation And The Hemodynamic Response Pnas From pnas.org
The common ground of these methods lies in using a specific form for the hemodynamic response function. When the Gamma Distribution is created with parameters to best fit the BOLD response observed by the majority of empirical studies we refer to it as the canonical Hemodynamic Response Function or HRF. This activation model is called hemodynamic response function HRF for the voxel and as well discuss in a later post can be estimated from the measured BOLD signals. An HRF is a function of time and usually peaks 4-6s afer the event onset. It is dependent on cerebrovascular reactivity and neurovascular coupling1 Most studies assume a standard whole-brain canonical HRF during analysis typically made of 2 gamma functions although previous works show HRF variability for different brain regions and across subjects25 The variability of non-neural. Lets assume for now that the voxel is also activated to an equal degree to all stimuli.
The common ground of these methods lies in using a specific form for the hemodynamic response function.
Obtain a measure of changes in the level of blood oxygenation over time. Modeling HRF is essential to identifying. Such temporal change of MR signal is called Hemodynamic response function. This increase occurs first in the region that is active but then moves downstream from this area. HRF variability HRFv across the brain could in principle alter functional connectivity FC estimates from restingstate fMRI rsfMRI. As described briefly in The Hemodynamic Response Function section arterioles and arteries dilate with brain activation causing an increase in blood flow volume and oxygenation.
 Source: andysbrainbook.readthedocs.io
Source: andysbrainbook.readthedocs.io
Our function will accept an array that gives the times we want to calculate the HRF for and returns the values of the HRF for those times. In order to obtain estimates of. It can be used to capture the response of the brain to various tasks. However this is obviously harder to do for higher order cortices such as prefrontal areas. Based on principals of blood oxygenation level dependent BOLD effect MR signals raised according to brain neural activity.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The shape of the HRF is controlled by both neural and non-neural factors. Hemodynamic response function HRF. Since HRF is influenced by non-neural factors to date it has largely been considered as a. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI is a medical-imaging technique for studying brain function. There is evidence that the hemodynamic response function is different in awake compared to anesthetized preparations.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
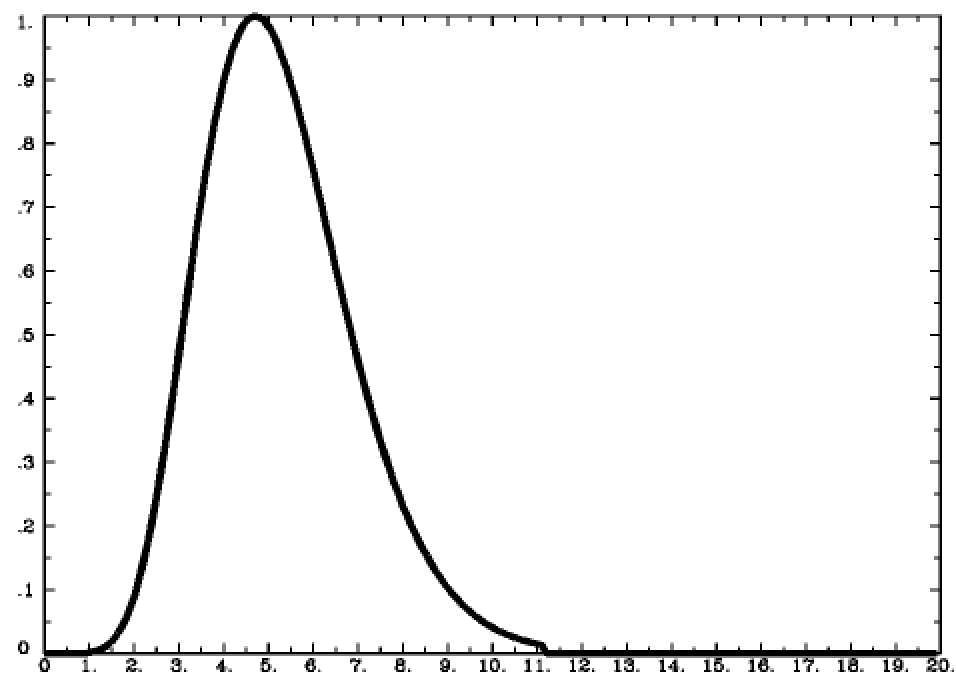
An HRF is a function of time and usually peaks 4-6s afer the event onset. An HRF is a function of time and usually peaks 4-6s afer the event onset. As such the HRF has been shown to vary across brain regions and individuals. It is dependent on cerebrovascular reactivity and neurovascular coupling1 Most studies assume a standard whole-brain canonical HRF during analysis typically made of 2 gamma functions although previous works show HRF variability for different brain regions and across subjects25 The variability of non-neural. However this is obviously harder to do for higher order cortices such as prefrontal areas.
 Source: andysbrainbook.readthedocs.io
Source: andysbrainbook.readthedocs.io
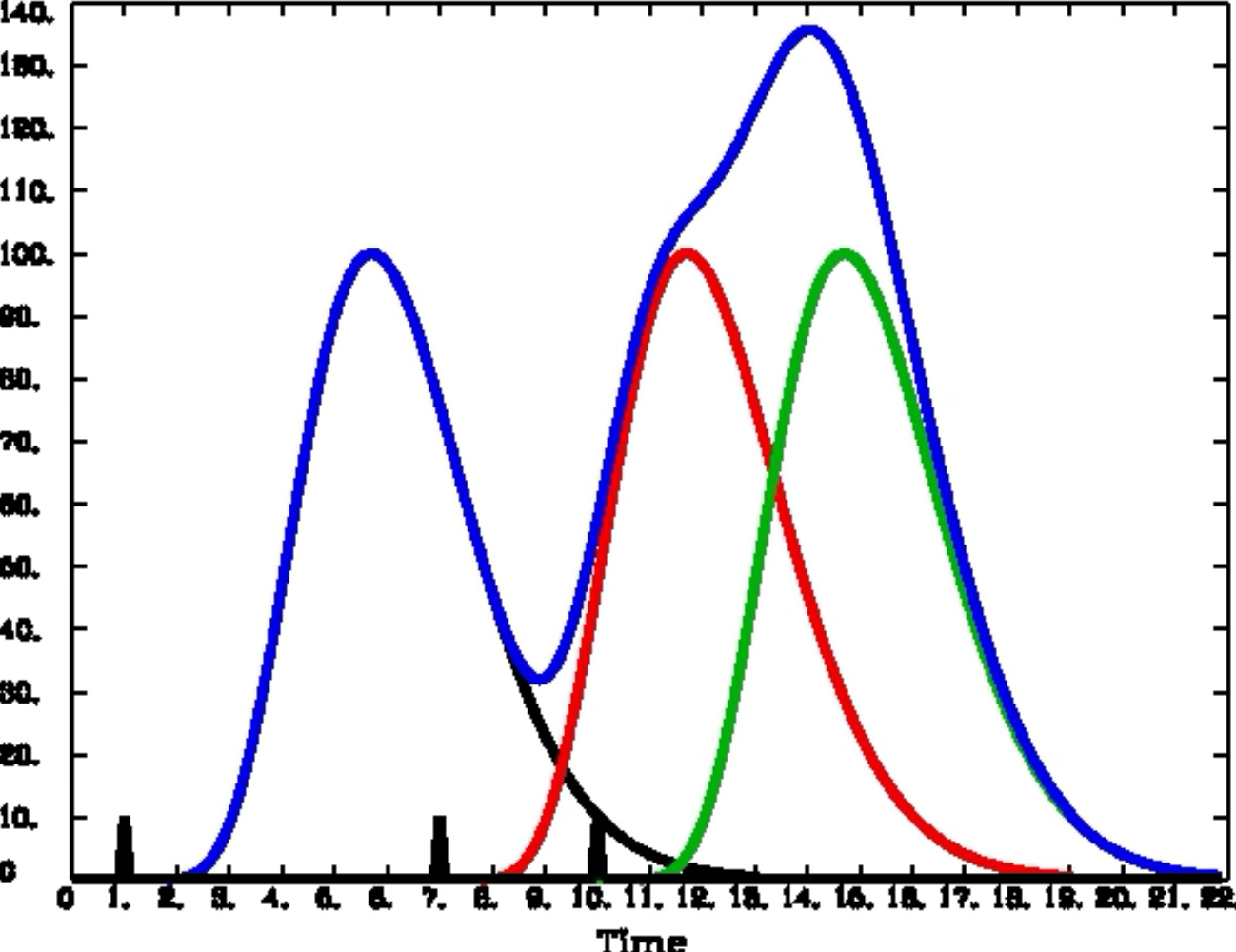
The hemodynamic response function HRF represents the transfer function linking neural activity with the functional MRI fMRI signal modeling neurovascular coupling. HRF models have been derived for sensory areas where it is relatively clear what events cause a neural impulse response. Our function will accept an array that gives the times we want to calculate the HRF for and returns the values of the HRF for those times. Neural field potential responses were also recorded and in the awake animals a linear neuralhemodynamic coupling relationship was found while in anesthetized animals this relationship was nonlinear over the range of responses recorded. Functional MRI is based on changes in cerebral microvasculature triggered by increased neuronal oxidative metabolism.
 Source: andysbrainbook.readthedocs.io
Source: andysbrainbook.readthedocs.io
It can be used to capture the response of the brain to various tasks. This change in blood flow follows a pattern known as the hemodynamic response function HRF which typically peaks 4-6 s following stimulus delivery. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI is a medical-imaging technique for studying brain function. Our function will accept an array that gives the times we want to calculate the HRF for and returns the values of the HRF for those times. The shape of the HRF is controlled by both neural and non-neural factors.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Neural field potential responses were also recorded and in the awake animals a linear neuralhemodynamic coupling relationship was found while in anesthetized animals this relationship was nonlinear over the range of responses recorded. In order to obtain estimates of. Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is an indirect measure of brain activity ie. We call it a basis function because it is the fundamental element or basis of the model we will create and fit to the time series of. The Hemodynamic Response Function HRF is a mathematical characterization of the change in blood oxygenation subsequent to activation Jezzard 2001.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
As described briefly in The Hemodynamic Response Function section arterioles and arteries dilate with brain activation causing an increase in blood flow volume and oxygenation. As described briefly in The Hemodynamic Response Function section arterioles and arteries dilate with brain activation causing an increase in blood flow volume and oxygenation. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI is a medical-imaging technique for studying brain function. We call it a basis function because it is the fundamental element or basis of the model we will create and fit to the time series of. The hemodynamic response function HRF represents the transfer function linking neural activity with the functional MRI fMRI signal modeling neurovascular coupling.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Hemodynamic response function A hemodynamic response function HRF is used to model the temporal evoluation of an fMRI response to an experimental event. Obtain a measure of changes in the level of blood oxygenation over time. Accurately model the hemodynamic response function HRF ie the hemodynamic response evoked by a punctuate neural event. This activation model is called hemodynamic response function HRF for the voxel and as well discuss in a later post can be estimated from the measured BOLD signals. Since HRF is influenced by non-neural factors to date it has largely been considered as a.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI has been used to infer age-differences in neural activity from the hemodynamic response function HRF that characterizes the blood-oxygen-level-dependent BOLD signal over time. Since HRF is influenced by non-neural factors to date it has largely been considered as a. Neural field potential responses were also recorded and in the awake animals a linear neuralhemodynamic coupling relationship was found while in anesthetized animals this relationship was nonlinear over the range of responses recorded. The response to a brief intense period of neural stimulation is called the hemodynamic response function HRF. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI is a medical-imaging technique for studying brain function.

This activation model is called hemodynamic response function HRF for the voxel and as well discuss in a later post can be estimated from the measured BOLD signals. Accurate estimates of the BOLD hemodynamic response function HRF are crucial for the interpretation and analysis of event-related functional MRI data. Based on principals of blood oxygenation level dependent BOLD effect MR signals raised according to brain neural activity. Accurately model the hemodynamic response function HRF ie the hemodynamic response evoked by a punctuate neural event. It can be used to capture the response of the brain to various tasks.

Based on principals of blood oxygenation level dependent BOLD effect MR signals raised according to brain neural activity. Hemodynamic response function A hemodynamic response function HRF is used to model the temporal evoluation of an fMRI response to an experimental event. Constructing a hemodynamic response function We can use these gamma functions to construct a continuous function that is close to the hemodynamic response we observe for a single brief event in the brain. The response to a brief intense period of neural stimulation is called the hemodynamic response function HRF. When the Gamma Distribution is created with parameters to best fit the BOLD response observed by the majority of empirical studies we refer to it as the canonical Hemodynamic Response Function or HRF.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
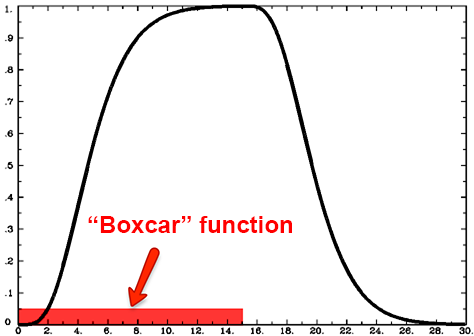
Obtain a measure of changes in the level of blood oxygenation over time. Lets assume for now that the voxel is also activated to an equal degree to all stimuli. The fMRI task design has a considerable effect on the efficiency and detection power of the study. Accurately model the hemodynamic response function HRF ie the hemodynamic response evoked by a punctuate neural event. An HRF is a function of time and usually peaks 4-6s afer the event onset.
 Source: biorxiv.org
Source: biorxiv.org
Accurately model the hemodynamic response function HRF ie the hemodynamic response evoked by a punctuate neural event. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI is a medical-imaging technique for studying brain function. We call it a basis function because it is the fundamental element or basis of the model we will create and fit to the time series of. The Hemodynamic Response Function HRF is a mathematical characterization of the change in blood oxygenation subsequent to activation Jezzard 2001. The common ground of these methods lies in using a specific form for the hemodynamic response function.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The hemodynamic response function HRF represents the transfer function linking neural activity with the functional MRI fMRI signal modeling neurovascular coupling. In order to obtain estimates of. Obtain a measure of changes in the level of blood oxygenation over time. HRF models have been derived for sensory areas where it is relatively clear what events cause a neural impulse response. The response to a brief intense period of neural stimulation is called the hemodynamic response function HRF.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
It is dependent on cerebrovascular reactivity and neurovascular coupling1 Most studies assume a standard whole-brain canonical HRF during analysis typically made of 2 gamma functions although previous works show HRF variability for different brain regions and across subjects25 The variability of non-neural. HRF variability HRFv across the brain could in principle alter functional connectivity FC estimates from restingstate fMRI rsfMRI. Our function will accept an array that gives the times we want to calculate the HRF for and returns the values of the HRF for those times. This activation model is called hemodynamic response function HRF for the voxel and as well discuss in a later post can be estimated from the measured BOLD signals. This increase occurs first in the region that is active but then moves downstream from this area.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Accurate estimates of the BOLD hemodynamic response function HRF are crucial for the interpretation and analysis of event-related functional MRI data. The response to a brief intense period of neural stimulation is called the hemodynamic response function HRF. We call it a basis function because it is the fundamental element or basis of the model we will create and fit to the time series of. HRF variability HRFv across the brain could in principle alter functional connectivity FC estimates from restingstate fMRI rsfMRI. Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is an indirect measure of brain activity ie.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
It can be used to capture the response of the brain to various tasks. Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is an indirect measure of brain activity ie. Such temporal change of MR signal is called Hemodynamic response function. HRF models have been derived for sensory areas where it is relatively clear what events cause a neural impulse response. Hemodynamic response function HRF.
 Source: math.mcgill.ca
Source: math.mcgill.ca
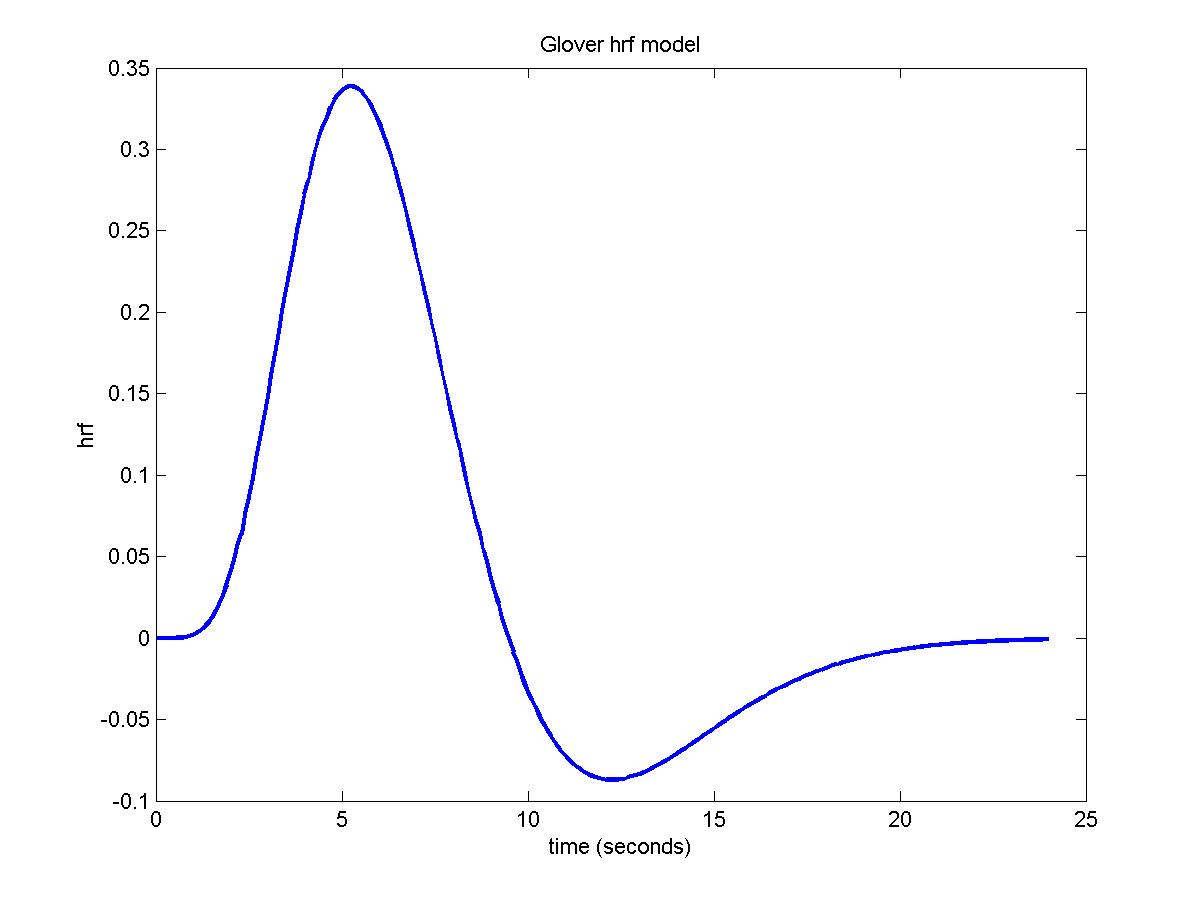
Constructing a hemodynamic response function We can use these gamma functions to construct a continuous function that is close to the hemodynamic response we observe for a single brief event in the brain. However the nature of the hemodynamic response to interictal spikes has not been fully described although some preliminary results have been presented Bagshaw et al 2004. We call it a basis function because it is the fundamental element or basis of the model we will create and fit to the time series of. The Hemodynamic Response Function HRF is a mathematical characterization of the change in blood oxygenation subsequent to activation Jezzard 2001. FMRI is the convolution of the hemodynamic response function HRF and unmeasured neural activity.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title hemodynamic response function by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.