Dolichoectatic basilar artery
Home » » Dolichoectatic basilar arteryYour Dolichoectatic basilar artery images are ready in this website. Dolichoectatic basilar artery are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Dolichoectatic basilar artery files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for dolichoectatic basilar artery pictures information linked to the dolichoectatic basilar artery keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our website always provides you with hints for viewing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Dolichoectatic Basilar Artery. The foregoing terms may include synonyms similar disorders variations in usage and abbreviations. Dolichoectasia is a rare disorder of the cerebral vasculature consisting of vascular elongation widening and tortuosity usually involving the vertebral and basilar arteries. Fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms occur in any of the intracranial arteries but particularly in the vertebrobasilar and internal carotid arteries. In patients with complex fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery this approach ultimately led to sacrifice of one or both vertebral arteries.
 Axial A T2w Magnetic Resonance Imaging Image Show The Flow Void Of Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Axial A T2w Magnetic Resonance Imaging Image Show The Flow Void Of Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Dolichoectatic basilar artery has become a more frequent finding in patients examined with modern neuroimaging techniques. 15 reviewed the natural history of large complex posterior circulation aneurysms including dolichoectatic lesions within the accumulated case series by Drake and Peerless 3 and found that 80 of patients had died or were severely disabled by the 5. They can be detected incidentally or present with neurologic complications including ischemic stroke intracranial hemorrhage or compression of surrounding neural structures. We report cerebral artery involvement in three French patients with late-onset Pompe disease. Fusiform dolichoectatic basilar artery aneurysms are dangerous vascular entities that are believed to signify a poor prognosis. If the patient tolerated the parent vessel occlusion acutely collateralization of blood flow led to continued growth of the aneurysm and the patients eventual death.
Dolichoectatic basilar artery also produced hydrocephalus in one patient.
The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography. Dolichoectasia dilatative arteriopathy describes marked elongation widening and tortuosity of arteries. The foregoing terms may include synonyms similar disorders variations in usage and abbreviations. If the patient tolerated the parent vessel occlusion acutely collateralization of blood flow led to continued growth of the aneurysm and the patients eventual death. Cranial nerve dysfunction such as TN can occur late in the natural history of the disease when there is significant elongation of the basilar artery BA and aneurysm expansion. Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia Is Associated With Paramedian Pontine Infarction Ectasia of the BA other than elongation or angulation appears to contribute to the occurrence of PPI.
 Source: neurologyindia.com
Source: neurologyindia.com
They can be detected incidentally or present with neurologic complications including ischemic stroke intracranial hemorrhage or compression of surrounding neural structures. Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia Is Associated With Paramedian Pontine Infarction Ectasia of the BA other than elongation or angulation appears to contribute to the occurrence of PPI. The intracranial vertebral and basilar arteries are preferentially involved. The foregoing terms may include synonyms similar disorders variations in usage and abbreviations. Dolichoectatic basilar artery also produced hydrocephalus in one patient.
 Source: e-jnc.org
Source: e-jnc.org
15 reviewed the natural history of large complex posterior circulation aneurysms including dolichoectatic lesions within the accumulated case series by Drake and Peerless 3 and found that 80 of patients had died or were severely disabled by the 5. Dolichoectatic arteries usually have an abnormally large external diameter and a thin arterial wall with degenerat. The foregoing terms may include synonyms similar disorders variations in usage and abbreviations. 15 reviewed the natural history of large complex posterior circulation aneurysms including dolichoectatic lesions within the accumulated case series by Drake and Peerless 3 and found that 80 of patients had died or were severely disabled by the 5. A dilative arteriopathy complicated with carotid artery dissection was diagnosed in the third patient aged 50 years.
 Source: medlink.com
Source: medlink.com
Arteriopathy basilar artery ectasia s-aneurysm and tortuous basilar artery. Diagnostic criteria and prognosis studies of IADE are based on basilar artery diameter which is a good quantitative marker for the severity of the disease. Dolichoectatic basilar artery also produced hydrocephalus in one patient. Dolichoectatic basilar artery has become a more frequent finding in patients examined with modern neuroimaging techniques. Described complications of basilar dolichoectasia include ischemic infarcts of the brainstem compression of cranial nerves and hydrocephalus.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Dolichoectatic basilar artery also produced hydrocephalus in one patient. Its neurological symptoms and signs are highly variable. Up to 12 of patients with stroke have intracranial arterial dolichoectasia IADE and the basilar artery is affected in 80 of these cases. Fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms occur in any of the intracranial arteries but particularly in the vertebrobasilar and internal carotid arteries. When this anomaly is diagnosed by CT findings even if it is clinically asymptomatic it may be better to treat these patients.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Fusiform dolichoectatic basilar artery aneurysms are dangerous vascular entities that are believed to signify a poor prognosis. We report cerebral artery involvement in three French patients with late-onset Pompe disease. The intracranial vertebral and basilar arteries are preferentially involved. Dolichoectatic basilar artery has become a more frequent finding in patients examined with modern neuroimaging techniques. Dolichoectatic arteries usually have an abnormally large external diameter and a thin arterial wall with degenerat.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Dolichoectasia dilatative arteriopathy describes marked elongation widening and tortuosity of arteries. We report cerebral artery involvement in three French patients with late-onset Pompe disease. Diagnostic criteria and prognosis studies of IADE are based on basilar artery diameter which is a good quantitative marker for the severity of the disease. Overview In this updated article the author reviews current knowledge about nonsaccular intracranial aneurysms including fusiform and dolichoectatic intracranial. They can be detected incidentally or present with neurologic complications including ischemic stroke intracranial hemorrhage or compression of surrounding neural structures.
Source:
We report cerebral artery involvement in three French patients with late-onset Pompe disease. If the patient tolerated the parent vessel occlusion acutely collateralization of blood flow led to continued growth of the aneurysm and the patients eventual death. When this anomaly is diagnosed by CT findings even if it is clinically asymptomatic it may be better to treat these patients. Arteriopathy basilar artery ectasia s-aneurysm and tortuous basilar artery. Overview In this updated article the author reviews current knowledge about nonsaccular intracranial aneurysms including fusiform and dolichoectatic intracranial.
 Source: scielo.br
Source: scielo.br
The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography. When this anomaly is diagnosed by CT findings even if it is clinically asymptomatic it may be better to treat these patients. We report cerebral artery involvement in three French patients with late-onset Pompe disease. The foregoing terms may include synonyms similar disorders variations in usage and abbreviations. Described complications of basilar dolichoectasia include ischemic infarcts of the brainstem compression of cranial nerves and hydrocephalus.
 Source: medlink.com
Source: medlink.com
15 reviewed the natural history of large complex posterior circulation aneurysms including dolichoectatic lesions within the accumulated case series by Drake and Peerless 3 and found that 80 of patients had died or were severely disabled by the 5. The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography. Trigeminal neuralgia TN secondary to a dolichoectatic basilar artery DBA is a rare phenomenon. Overview In this updated article the author reviews current knowledge about nonsaccular intracranial aneurysms including fusiform and dolichoectatic intracranial. Dolichoectatic basilar artery has become a more frequent finding in patients examined with modern neuroimaging techniques.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The dolichoectatic basilar artery is associated with various consequences especially in relation to the pathogenesis of brainstem infarction. In patients with complex fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery this approach ultimately led to sacrifice of one or both vertebral arteries. Fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms occur in any of the intracranial arteries but particularly in the vertebrobasilar and internal carotid arteries. The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography. The dolichoectatic basilar artery is associated with various consequences especially in relation to the pathogenesis of brainstem infarction.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
The mechanism of stroke may be due to penetrating artery occlusion basilar artery thrombosis or. Cranial nerve dysfunction such as TN can occur late in the natural history of the disease when there is significant elongation of the basilar artery BA and aneurysm expansion. Fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms occur in any of the intracranial arteries but particularly in the vertebrobasilar and internal carotid arteries. In patients with complex fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery this approach ultimately led to sacrifice of one or both vertebral arteries. Fusiform dolichoectatic basilar artery aneurysms are dangerous vascular entities that are believed to signify a poor prognosis.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
The dolichoectatic basilar artery is associated with various consequences especially in relation to the pathogenesis of brainstem infarction. If the patient tolerated the parent vessel occlusion acutely collateralization of blood flow led to continued growth of the aneurysm and the patients eventual death. We report cerebral artery involvement in three French patients with late-onset Pompe disease. The mechanism of stroke may be due to penetrating artery occlusion basilar artery thrombosis or. Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia Is Associated With Paramedian Pontine Infarction Ectasia of the BA other than elongation or angulation appears to contribute to the occurrence of PPI.
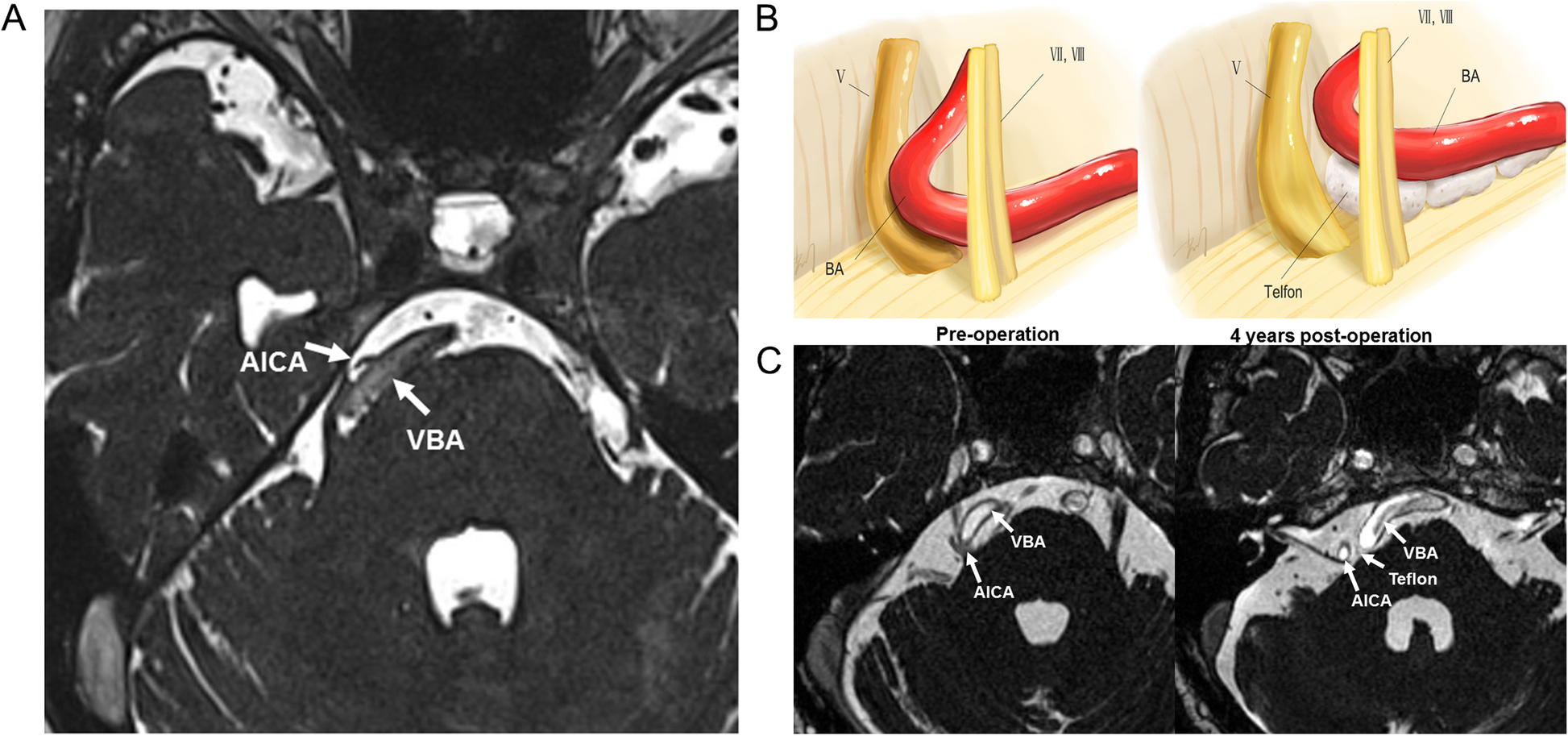 Source: bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com
Source: bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com
15 reviewed the natural history of large complex posterior circulation aneurysms including dolichoectatic lesions within the accumulated case series by Drake and Peerless 3 and found that 80 of patients had died or were severely disabled by the 5. The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography. Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia Is Associated With Paramedian Pontine Infarction Ectasia of the BA other than elongation or angulation appears to contribute to the occurrence of PPI. A dilative arteriopathy complicated with carotid artery dissection was diagnosed in the third patient aged 50 years. Overview In this updated article the author reviews current knowledge about nonsaccular intracranial aneurysms including fusiform and dolichoectatic intracranial.
 Source: ajnr.org
Source: ajnr.org
Overview In this updated article the author reviews current knowledge about nonsaccular intracranial aneurysms including fusiform and dolichoectatic intracranial. We report cerebral artery involvement in three French patients with late-onset Pompe disease. In patients with complex fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery this approach ultimately led to sacrifice of one or both vertebral arteries. They can be detected incidentally or present with neurologic complications including ischemic stroke intracranial hemorrhage or compression of surrounding neural structures. Up to 12 of patients with stroke have intracranial arterial dolichoectasia IADE and the basilar artery is affected in 80 of these cases.
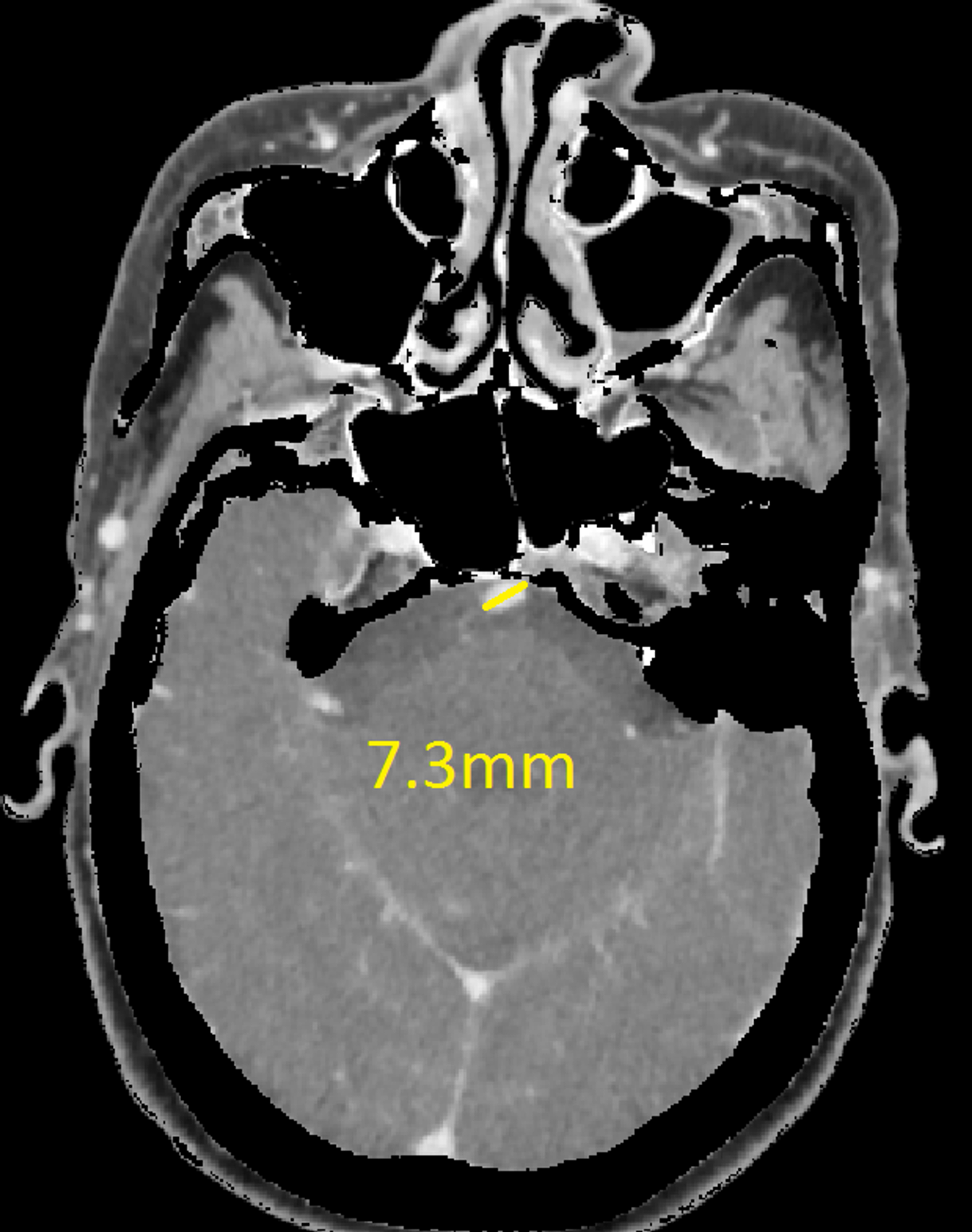 Source: cureus.com
Source: cureus.com
The intracranial vertebral and basilar arteries are preferentially involved. The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography. Dolichoectasia dilatative arteriopathy describes marked elongation widening and tortuosity of arteries. If the patient tolerated the parent vessel occlusion acutely collateralization of blood flow led to continued growth of the aneurysm and the patients eventual death. Fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms occur in any of the intracranial arteries but particularly in the vertebrobasilar and internal carotid arteries.
 Source: wajradiology.org
Source: wajradiology.org
Fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms occur in any of the intracranial arteries but particularly in the vertebrobasilar and internal carotid arteries. In patients with complex fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery this approach ultimately led to sacrifice of one or both vertebral arteries. A dilative arteriopathy complicated with carotid artery dissection was diagnosed in the third patient aged 50 years. Fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms occur in any of the intracranial arteries but particularly in the vertebrobasilar and internal carotid arteries. The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
The first patient died at age 35 years from complications of a giant fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery and her 34-year-old sister showed evidence of dolichoectatic basilar artery on magnetic resonance angiography. In patients with complex fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery this approach ultimately led to sacrifice of one or both vertebral arteries. If the patient tolerated the parent vessel occlusion acutely collateralization of blood flow led to continued growth of the aneurysm and the patients eventual death. Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia Is Associated With Paramedian Pontine Infarction Ectasia of the BA other than elongation or angulation appears to contribute to the occurrence of PPI. Dolichoectatic basilar artery has become a more frequent finding in patients examined with modern neuroimaging techniques.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Arteriopathy basilar artery ectasia s-aneurysm and tortuous basilar artery. Up to 12 of patients with stroke have intracranial arterial dolichoectasia IADE and the basilar artery is affected in 80 of these cases. Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia Is Associated With Paramedian Pontine Infarction Ectasia of the BA other than elongation or angulation appears to contribute to the occurrence of PPI. In patients with complex fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery this approach ultimately led to sacrifice of one or both vertebral arteries. A dilative arteriopathy complicated with carotid artery dissection was diagnosed in the third patient aged 50 years.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title dolichoectatic basilar artery by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.