Butyrivibrio crossotus low
Home » » Butyrivibrio crossotus lowYour Butyrivibrio crossotus low images are available. Butyrivibrio crossotus low are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Butyrivibrio crossotus low files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for butyrivibrio crossotus low pictures information related to the butyrivibrio crossotus low keyword, you have come to the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
Butyrivibrio Crossotus Low. Van Gylswyk et al. Abundance associated with higher bacterial richness in the gut. Green represents a low need for support and corresponds with scores less than 2 grey represents an optional need for support and corresponds with a score of 2 or 3 yellow indicates moderate need with scores of 4-6 and red indicates high need with scores of. Appear to be associated with a diet richer in complex carbohydrates than animal protein.
 Butyrivibrio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Butyrivibrio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Abundance associated with higher bacterial richness in the gut. Butyrivibrio crossotus are often found in the human gut and inversely associated with obesity. Van Gylswyk et al. Crossotus correlated with xylanasexylosidase enzymes that break down complex carbohydrates mainly from grains. A high-fiber diet can increase the abundance of Firmicutes and reduce the abundance of Bacteroides and consequently increase the concentration of short-chain fatty acids SCFAs in the intestine inhibiting the development of CRC Colorectal cancer. With a high Akkermansia Verrucomicrobia.
They are often found in the human gut.
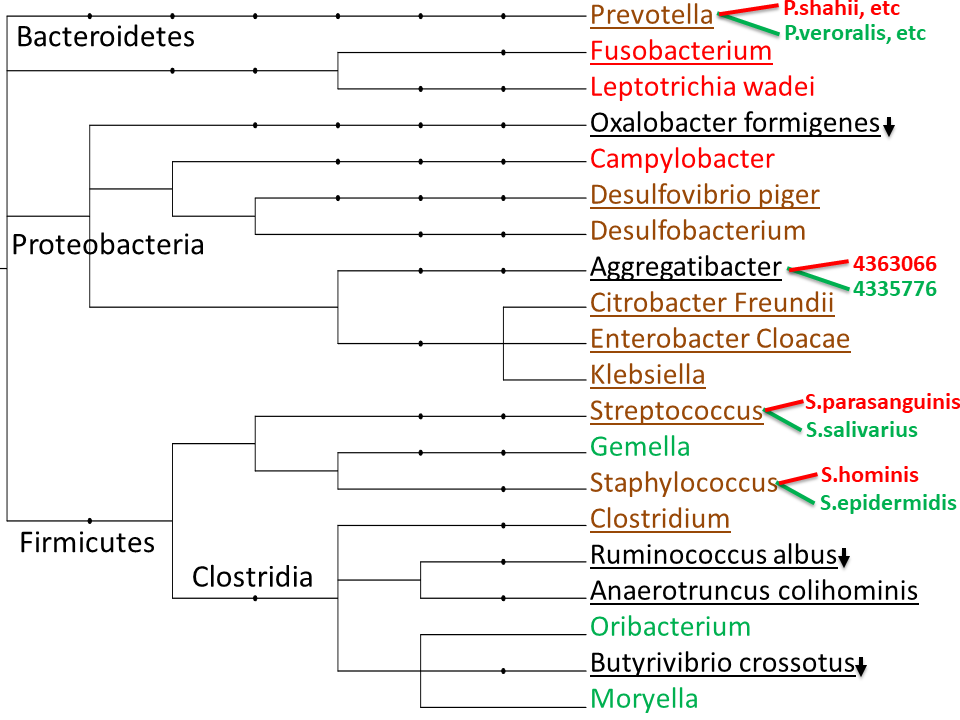
Bacteria Firmicutes Clostridia Clostridiales Lachnospiraceae Butyrivibrio. The key defining element favoring digestive health of the high gene count microbiome included increased proportion of butyrate-producing organisms increased production of. The high gene count microbiome included Anaerotruncus colihominis Butyrivibrio crossotus Akkermansia sp and Fecalibacterium sp. The genus name Butyrivibrio means vibrating curved rod and the species name crossotus means tassled both describing the shape of these microbes and how they move by vibrating tiny hair-like appendages called flagella. Bacteria Firmicutes Clostridia Clostridiales Lachnospiraceae Butyrivibrio. Genetically related to B.

Firmicutes - Clostridia - Clostridiales - Lachnospiraceae - Butyrivibrio - Butyrivibrio crossotus. Decreased in metabolic disorders. IMHO the most likely way to get a low level up is by eliminating what is killing them. Lophotrichous Butyrivibrio crossotus from the human gut Moore et al 1976. The genus name Butyrivibrio means vibrating curved rod and the species name crossotus means tassled both describing the shape of these microbes and how they move by vibrating tiny hair-like appendages called flagella.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Butyrivibrio strains isolated from human fecal material differ in substrate utilization and flagellar arrangement from B. Fibrisolvens isolates Forster et al. These strains have been designated as B. Go to DataPunkNet and see what bacteria inhibits them feed them. And lactate-producing Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis Van Gylswyk et al 1996 from the rumen.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Increased in overweight men drinking low glycinin soymilk compared to regular Higher counts10 of Butyrivibrio spp. Fibrisolvens isolates Forster et al. Van Gylswyk et al. For grand parent we have. Taxonomically it belongs in the clostridial rRNA subcluster XIVa and is a member of the family Lachnospiraceae 11.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Similar variations have been observed in butyrate-producing bacteria from the human gut Barcenilla et al 2000. The genus name Butyrivibrio means vibrating curved rod and the species name crossotus means tassled both describing the shape of these microbes and how they move by vibrating tiny hair-like appendages called flagella. The type strain ATCC 19171 is actually atypical of the great majority of B. Similar variations have been observed in butyrate-producing bacteria from the human gut Barcenilla et al 2000. Taxonomically it belongs in the clostridial rRNA subcluster XIVa and is a member of the family Lachnospiraceae 11.

Butyrivibrio crossotus Low Dialister invisus Low Lactobacillus Low Ruminococcus albus Low uBiome Inc. Firmicutes - Clostridia - Clostridiales - Lachnospiraceae - Butyrivibrio - Butyrivibrio crossotus. Butyrivibrio crossotus are often found in the human gut and inversely associated with obesity. Bacteria Firmicutes Clostridia Clostridiales Lachnospiraceae Butyrivibrio. Abundance associated with higher bacterial richness in the gut.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Collinsella Barnesellia Akkermansia muciniphila were lower in dry eye patients compared to normal patients. Butyrivibrio crossotus is not known to be associated with any disorder. Decreased in metabolic disorders. Fibrisolvens isolates Forster et al. Collinsella Barnesellia Akkermansia muciniphila were lower in dry eye patients compared to normal patients.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Green represents a low need for support and corresponds with scores less than 2 grey represents an optional need for support and corresponds with a score of 2 or 3 yellow indicates moderate need with scores of 4-6 and red indicates high need with scores of. Butyrivibrio crossotus are often found in the human gut and inversely associated with obesity. Bacteria Firmicutes Clostridia Clostridiales Lachnospiraceae Butyrivibrio. The key defining element favoring digestive health of the high gene count microbiome included increased proportion of butyrate-producing organisms increased production of. A high-fiber diet can increase the abundance of Firmicutes and reduce the abundance of Bacteroides and consequently increase the concentration of short-chain fatty acids SCFAs in the intestine inhibiting the development of CRC Colorectal cancer.
 Source: fishmanvision.com
Source: fishmanvision.com
These strains have been designated as B. Abundance associated with higher bacterial richness in the gut. A high-fiber diet can increase the abundance of Firmicutes and reduce the abundance of Bacteroides and consequently increase the concentration of short-chain fatty acids SCFAs in the intestine inhibiting the development of CRC Colorectal cancer. 360 Langton Street San Francisco CA 94103 Phone Fax Email 502 298-4349 415 965-4261 cl i ent srv ub om. They are often found in the human gut.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
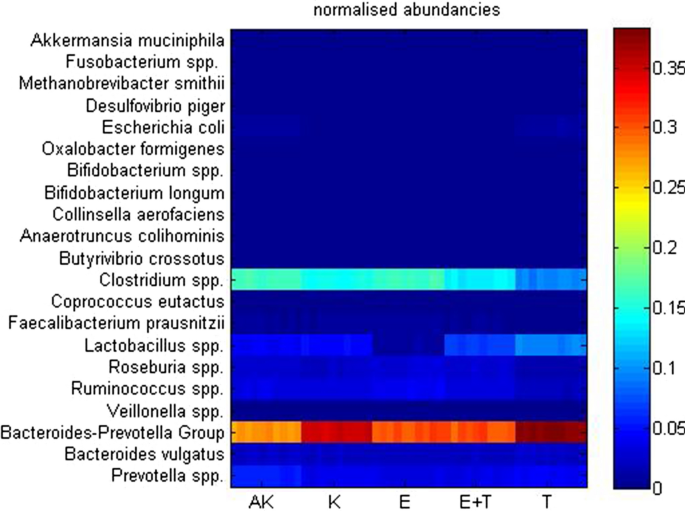
Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316 T formerly Clostridium proteoclasticum is a Gram positive polysaccharide-degrading butyrate-producing anaerobic bacterium isolated from the bovine rumen. And lactate-producing Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis Van Gylswyk et al 1996 from the rumen. Butyrivibrio crossotus Low Dialister invisus Low Lactobacillus Low Ruminococcus albus Low uBiome Inc. These observations are illustrated in Figure 1. IMHO the most likely way to get a low level up is by eliminating what is killing them.
 Source: blog.healthmatters.io
Source: blog.healthmatters.io
Butyrivibrio is a genus of bacteria in Class Clostridia. Increased in overweight men drinking low glycinin soymilk compared to regular Higher counts10 of Butyrivibrio spp. Most of the studies deal with rumens cows etc DataPubNet. What does it mean if your FirmicutesBacteroidetes FB Ratio result is too low. Taxonomically it belongs in the clostridial rRNA subcluster XIVa and is a member of the family Lachnospiraceae 11.
 Source: microbiologyresearch.org
Source: microbiologyresearch.org
Most of the studies deal with rumens cows etc DataPubNet. Fibrisolvens isolates Forster et al. Collinsella Barnesellia Akkermansia muciniphila were lower in dry eye patients compared to normal patients. In some cases you may have to click up from species to strains to find information. Appear to be associated with a diet richer in complex carbohydrates than animal protein.
 Source: aurametrix.weebly.com
Source: aurametrix.weebly.com
1996 which include species names Butyrivibrio hungatei Butyrivibrio crossotus Clostridium proteoclasticum Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis and Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans Moore et al. Of these eight species were significantly reduced Akkermansia muciniphila Alistipes finegoldii Alistipes shahii Bacteroides faecis Bacteroides intestinalis Butyrivibrio crossotus Bacteroides stercoris and Prevotella stercorea while two were significantly increased before death Bifidobacterium longum and. Firmicutes - Clostridia - Clostridiales - Lachnospiraceae - Butyrivibrio - Butyrivibrio crossotus. Analysis revealed significant changes in the abundance of ten bacterial species before death. Similar variations have been observed in butyrate-producing bacteria from the human gut Barcenilla et al 2000.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
1996 which include species names Butyrivibrio hungatei Butyrivibrio crossotus Clostridium proteoclasticum Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis and Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans Moore et al. The high gene count microbiome included Anaerotruncus colihominis Butyrivibrio crossotus Akkermansia sp and Fecalibacterium sp. And lactate-producing Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis Van Gylswyk et al 1996 from the rumen. Green represents a low need for support and corresponds with scores less than 2 grey represents an optional need for support and corresponds with a score of 2 or 3 yellow indicates moderate need with scores of 4-6 and red indicates high need with scores of. 1996 which include species names Butyrivibrio hungatei Butyrivibrio crossotus Clostridium proteoclasticum Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis and Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans Moore et al.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Decreased in metabolic disorders. Appear to be associated with a diet richer in complex carbohydrates than animal protein. Hence the name Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens is quite descriptive Bryant and Small 1956a. Butyrivibrio crossotus INHIBITED BY. A high-fiber diet can increase the abundance of Firmicutes and reduce the abundance of Bacteroides and consequently increase the concentration of short-chain fatty acids SCFAs in the intestine inhibiting the development of CRC Colorectal cancer.
 Source: blog.healthmatters.io
Source: blog.healthmatters.io
Butyrivibrio crossotus Ruminococcus albus and Dialister invisus were low in 100 44 of non-dry eye patients and 92 1213 of dry eye patients. Bacteria Firmicutes Clostridia Clostridiales Lachnospiraceae Butyrivibrio. Abundance associated with higher bacterial richness in the gut Abundance may help protect against weight gain. With a high Akkermansia Verrucomicrobia. UBiomes Smart Gut associate low levels with various conditions.

Genetically related to B. Prebiotic Potential of Herbal Medicines Used in Digestive Health and Disease. Hence the name Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens is quite descriptive Bryant and Small 1956a. Butyrivibrio crossotus Low Dialister invisus Low Lactobacillus Low Ruminococcus albus Low uBiome Inc. With a high Akkermansia Verrucomicrobia.
 Source: blog.healthmatters.io
Source: blog.healthmatters.io
The high gene count microbiome included Anaerotruncus colihominis Butyrivibrio crossotus Akkermansia sp and Fecalibacterium sp. The genus name Butyrivibrio means vibrating curved rod and the species name crossotus means tassled both describing the shape of these microbes and how they move by vibrating tiny hair-like appendages called flagella. Fibrisolvens isolates Forster et al. Similar variations have been observed in butyrate-producing bacteria from the human gut Barcenilla et al 2000. Taxonomically it belongs in the clostridial rRNA subcluster XIVa and is a member of the family Lachnospiraceae 11.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Butyrivibrio strains isolated from human fecal material differ in substrate utilization and flagellar arrangement from B. Van Gylswyk et al. Lophotrichous Butyrivibrio crossotus from the human gut Moore et al 1976. 1996 which include species names Butyrivibrio hungatei Butyrivibrio crossotus Clostridium proteoclasticum Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis and Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans Moore et al. The key defining element favoring digestive health of the high gene count microbiome included increased proportion of butyrate-producing organisms increased production of.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title butyrivibrio crossotus low by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.